Hammick reaction
Nowadays, Hammick reaction has acquired important relevance in today's society. Whether due to its impact on popular culture, its influence on political decision-making or its relevance in the scientific field, Hammick reaction has captured the attention of people of all ages and backgrounds. In this article, we will thoroughly explore the phenomenon of Hammick reaction and its impact on different aspects of daily life. From its origins to its evolution today, we will analyze in detail how Hammick reaction has left its mark on society and how it continues to affect our daily lives.
| Hammick reaction | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Dalziel Hammick |
| Reaction type | Coupling reaction |
The Hammick reaction, named after Dalziel Hammick, is a chemical reaction in which the thermal decarboxylation of α-picolinic (or related) acids in the presence of carbonyl compounds forms 2-pyridyl-carbinols.[1][2][3]
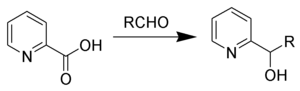
Using p-cymene as solvent has been shown to increase yields.[4]
Reaction mechanism
Upon heating α-picolinic acid will spontaneously decarboxylate forming the so-called 'Hammick Intermediate' (3). This was initially thought to be an aromatic ylide, but is now believed to be a carbene[5][6] In the presence of a strong electrophile, such as an aldehyde or ketone, this species will undergo nucleophilic attack faster than proton transfer. After nucleophilic attack intramolecular proton transfer yields the desired carbinol (6).

The scope of the reaction is effectively limited to decarboxylating acids where the carboxyl group is α to the nitrogen, (reactivity has been reported when the acids are located elsewhere on the molecule but with low yields)[7][8] thus suitable substrates are limited to the derivatives of α-picolinic acid[3][9] including the α-carboxylic acids of quinoline and isoquinoline.
See also
References
- ^ Dyson, P.; Hammick, D. L. (1937). "362. Experiments on the mechanism of decarboxylation. Part I. Decomposition of quinaldinic and isoquinaldinic acids in the presence of compounds containing carbonyl groups". J. Chem. Soc.: 1724. doi:10.1039/jr9370001724.
- ^ Hammick, D. L.; Dyson, P. (1939). "172. The mechanism of decarboxylation. Part II. The production of cyanide-like ions from α-picolinic, quinaldinic, and isoquinaldinic acids". J. Chem. Soc.: 809–812. doi:10.1039/jr9390000809.
- ^ a b Brown, E. V.; Shambhu, M. B. (1971). "Hammick reaction of methoxypyridine-2-carboxylic acids with benzaldehyde. Preparation of methoxy-2-pyridyl phenyl ketones". J. Org. Chem. 36 (14): 2002. doi:10.1021/jo00813a034.
- ^ Sperber, N.; Papa, D.; Schwenk, E.; Sherlock, M. (1949). "Pyridyl-Substituted Alkamine Ethers as Antihistaminic Agents". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 71 (3): 887–90. doi:10.1021/ja01171a034. PMID 18113525.
- ^ Hollóczki, Oldamur; Nyulászi, László (July 2008). "Stabilizing the Hammick Intermediate". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 73 (13): 4794–4799. doi:10.1021/jo8000035. PMID 18543975.
- ^ Lavorato, David; Terlouw, Johan K.; Dargel, Thomas K.; Koch, Wolfram; McGibbon, Graham A.; Schwarz, Helmut (1 January 1996). "Observation of the Hammick Intermediate: Reduction of the Pyridine-2-ylid Ion in the Gas Phase". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 118 (47): 11898–11904. doi:10.1021/ja961954l.
- ^ Mislow, Kurt (October 1947). "An Extension of the Scope of the Hammick Reaction". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 69 (10): 2559. doi:10.1021/ja01202a508.
- ^ Betts, M. J.; Brown, B. R. (1967). "Extension of the Hammick reaction to 2-pyridylacetic acid". Journal of the Chemical Society C: Organic: 1730. doi:10.1039/J39670001730.
- ^ Cantwell, Nelson H.; Brown, Ellis V. (March 1953). "An Investigation of the Hammick Reaction". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 75 (6): 1489–1490. doi:10.1021/ja01102a515.